Image Generated Using DALL-E
Semiconductor And Economy:
The semiconductor industry is a cornerstone, powering everything from smartphones to supercomputers. As this industry further grows, understanding the economic dimensions of it becomes increasingly critical.
To capture this essence, introducing Seminometrics, an interdisciplinary field that combines the intricate technology of semiconductors with the analytical precision of econometrics.
What is Seminometrics:
Seminometrics is the fusion of semiconductor technology and econometrics. While semiconductors are the essential components in electronic devices, econometrics involves the application of statistical and mathematical methods to economic data. This innovative approach provides a comprehensive lens to examine and interpret the economic impact of semiconductors, delivering significant benefits for researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders by offering valuable insights.
Semiconductor Industry: The sector focuses on designing and manufacturing semiconductor devices like chips and transistors, essential for electronic devices
Econometrics: The application of statistical and mathematical methods to economic data to analyze and forecast economic trends
Seminometrics: An interdisciplinary field combining semiconductor technology with econometric analysis to understand and optimize the economic impact of the semiconductor industry
By combining these fields, Seminometrics aims to provide a deeper understanding of the economic dynamics driving the semiconductor industry. This includes analyzing market trends, investment strategies, production efficiencies, and the global economic impact of semiconductor advancements.
Why Understand The Economics Of Semiconductors:
Understanding the economics of semiconductors is crucial for several reasons. It drives innovation and economic growth by supporting technological advancements. Analyzing financial trends and potential returns makes informed investment decisions possible. Companies can better navigate market dynamics and consumer demands, while governments can craft effective regulations and trade policies.
Conversely, robust supply chain management ensures efficient production and risk management. Understanding labor market trends guides workforce development, and sustainability is achieved by balancing economic growth with environmental and social responsibility. By capturing all these factors, stakeholders can make informed decisions that foster a robust and sustainable semiconductor industry.
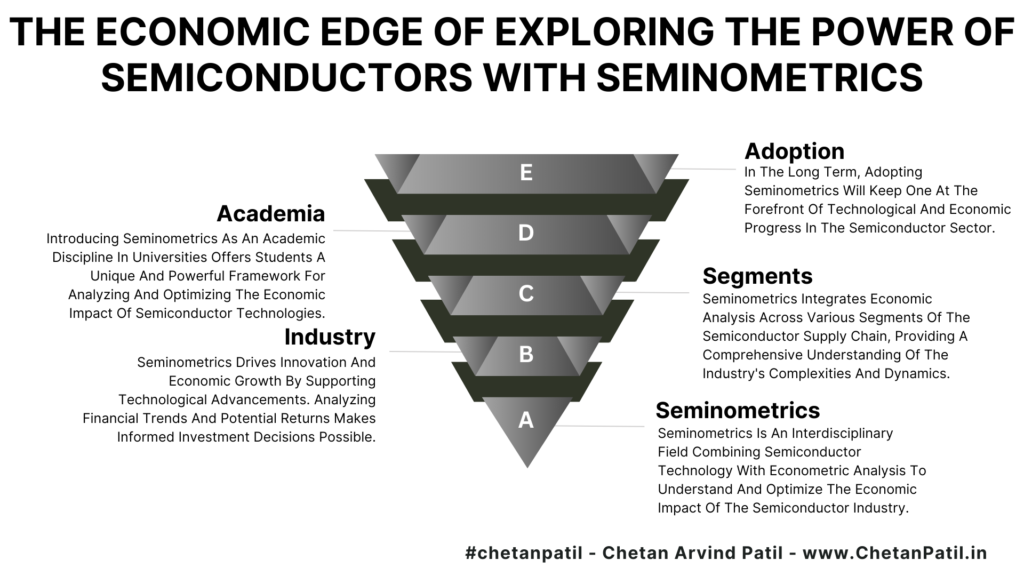
How Seminometrics Integrates Across Different Part Of Semiconductor Supply Chain:
Seminometrics, as an interdisciplinary field, integrates economic analysis across various segments of the semiconductor supply chain, providing a comprehensive understanding of the industry’s complexities and dynamics. By merging semiconductor technology with econometric methods, Seminometrics offers valuable insights into multiple critical areas:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Analysis | The semiconductor market is highly dynamic, characterized by rapid technological advancements and shifting consumer demands. Seminometrics helps stakeholders understand these trends, enabling them to make informed decisions about product development, pricing strategies, and market positioning. |
| Investment And Finance | Investment in the semiconductor industry is crucial for innovation and growth. Seminometrics provides tools to analyze investment patterns, assess financial performance, and predict future financial trends, guiding investors and companies in optimizing their financial strategies. |
| Production And Supply Chain | Efficient production and robust supply chains are vital for the semiconductor industry. Seminometrics examines cost structures, economies of scale, and supply chain dynamics, helping companies improve production processes and manage supply chain risks effectively. |
| Policy Impact | Government policies significantly influence the semiconductor industry, from research funding to trade regulations. Seminometrics evaluates the impact of these policies, aiding policymakers in crafting regulations that foster industry growth while balancing economic and social goals. |
| Innovation And RnD | Research and development are the lifeblood of the semiconductor industry. Seminometrics measures the returns on R&D investments and their impact on industry growth, helping companies allocate resources efficiently and drive innovation. |
| Labor Economics | The semiconductor industry relies on a skilled workforce. Seminometrics analyzes employment trends, wage dynamics, and the impact of automation, providing insights into workforce development and labor market policies. |
| Global Trade | The semiconductor industry is global, with complex trade relationships. Seminometrics investigates trade flows, comparative advantages, and the impact of trade policies, offering insights into global market dynamics and trade strategy. |
| Environmental And Social Impact | As sustainability becomes a priority, Seminometrics assesses the economic impact of environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives in the semiconductor industry, balancing economic growth with social responsibility. |
Integrating Seminometrics across the semiconductor supply chain gives stakeholders a holistic view of market trends, investment opportunities, production efficiencies, and global trade dynamics. This interdisciplinary approach enables informed decision-making, drives innovation, and promotes sustainable economic growth.
Teaching Seminometrics In Universities:
Introducing Seminometrics as an academic discipline in universities offers students a unique and powerful framework for analyzing and optimizing the economic impact of semiconductor technologies, a skillset that is becoming more and more in demand.
By integrating principles of semiconductor science with econometric techniques, Seminometrics can equip future professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to drive innovation and sustainable growth in this critical industry.
| Course Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction To Semiconductors | Cover the basics of semiconductor technology, including material science, chip design, and manufacturing processes. |
| Principles Of Economics And Econometrics | Provide a strong foundation in economics and econometrics, emphasizing data analysis, statistical methods, and economic modeling. |
| Market Dynamics And Financial Analysis | Focus on market dynamics and financial analysis specific to the semiconductor industry, using real-world case studies. |
| Policy And Global Trade Impact | Teach the impact of government policies, global trade, and international regulations on the semiconductor sector. |
| Research And Development In Semiconductors | Instruct on measuring and analyzing returns on R&D investments. |
| Practical Applications And Case Studies | Use practical applications and case studies to bridge theory and practice. |
Learning Seminometrics also provides students with a unique interdisciplinary skill set relevant to the modern economy. As future professionals in the semiconductor industry, students will benefit from a deep understanding of the field’s technological and economic aspects. This knowledge will enable them to make informed decisions, drive innovation, and contribute to sustainable economic growth.
Furthermore, expertise in Seminometrics will position students at the forefront of industry advancements, offering them a competitive edge in their careers and the ability to influence the future direction of semiconductor technology and its economic impact.
Take Away:
In summary, Seminometrics provides a robust framework for comprehending and harnessing the economic dynamics within the semiconductor industry. By merging the technological knowledge of semiconductor science with the analytical capabilities of econometrics, this interdisciplinary field offers critical insights that enable informed decision-making, spur innovation, and encourage sustainable economic development.
In the long term, adopting Seminometrics will keep one at the forefront of technological and economic progress in the semiconductor sector.