Photo by Tony Stoddard on Unsplash
In the hardware systems, the cache is used by Central Processing Units (CPU) to reduce the time which is required to access the data from the lower level memory like RAM. It does so by bringing the data beforehand (depending on the policy used) in the cache, which re-sides closer to the CPU.
This allows CPUs to perform calculations faster as the cycle time gets reduced and the latency is lowered. It also lowers the time and energy required to perform the computation task.
Same concept is applicable for the software systems, in which caching of data leads to faster access which reduces the response time and improves user experience. Content Delivery Network (CDN) is one of the best examples of software caching. Even web browsers use it.
However, both the hardware and the software caching systems are good from a data point of view, but not for computation. In the hardware systems, data is brought closer to the CPU for processing while in software systems the data is brought closer to the user after processing. For both the systems, if the source data is updated, then new data has to be fetched, which adds cost, time, and energy.
With the growing digital user base and improved connectivity around the world, the importance of caching is increasing to cater the data and computation demand.
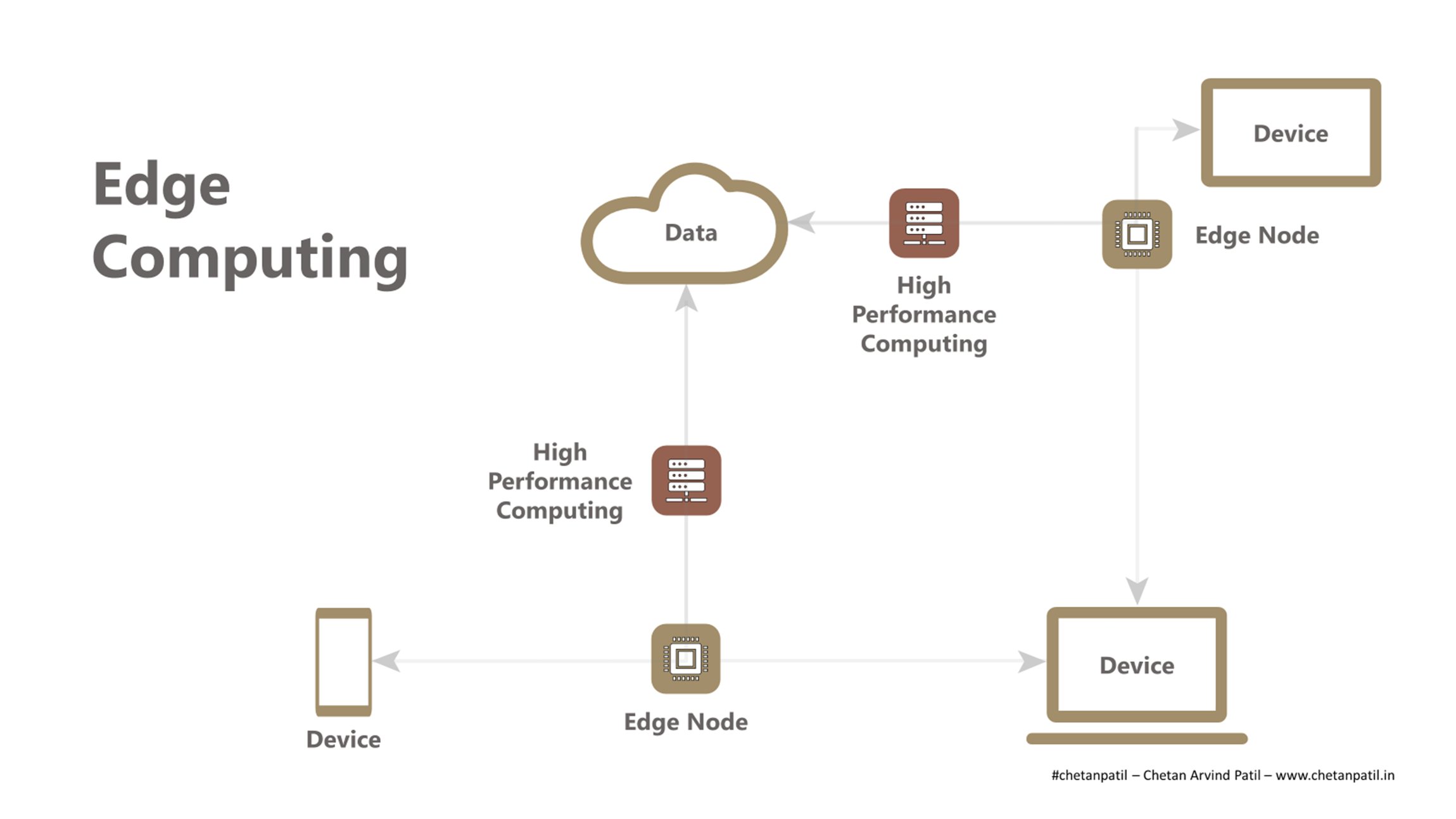
In order to serve this growing demand, the edge computing is being deployed. In a nutshell, the edge computing provides data and computation closer to the nodes requesting it with the help of widely deployed array of hardware. This leads to faster response time, reduces time to deliver the content, and provides massive distributed processing power.
EDGE COMPUTING BENEFITS
Large scale deployment of the edge computing is going to be a win-win situation for both the businesses and the consumers. The hardware and software deployment and development around the edge computing are also going to bring a tremendous amount of skill-based employment opportunities. The edge computing has numerous benefits. There are already several solutions from the semiconductor industry for the edge computing.
One of the important benefit of the edge computing is the computation speed. The edge computing can distribute the single task across different edge nodes, which reduces time to accomplish task. With 5G and Wi-Fi 6, the off-loading of the task to nearby edge nodes is going to ensure low latency and reliable service.
By reducing the number of hopes required to access the computation and data resources, the edge computing will also provide better security. The computation to be performed can be done by nearby nodes and the data to be accessed can also be stored at the same nodes. This process shields against any intruders trying to access the data by reducing the number of hops.

The edge computing is also designed to be scalable. There are no restrictions on the number of edge nodes that a specific network can hold, as long as the edge computing network is balancing the supply and demand requirement, and is not high on cost.
Adoption of 5G will be a gradual process. Consumers will take time to upgrade devices that are 5G compatible. To cater to the previous generation (2.5G/3G/4G) technology users, interoperability is important. The edge computing is capable of providing interoperability, thus both new and legacy devices can work with the same edge node.
The major application areas of the edge computing is going to be On-Device Artificial Intelligence (AI), which will allow smart devices (smartphones, cameras, sensors, etc.) to off-load the compute intensive task to the nearby edge nodes.
The edge computing will take digital experience to the next level.
EDGE COMPUTING OPPORTUNITIES
Every new technological solution presents new opportunities for the businesses. Consumers also gain due to the new products and services. From a business point of view, the edge computing provides several ways to generate revenue.
The edge computing will drive the introduction of new products. Both software and hardware solutions will be introduced. Businesses can explore the edge computing in form of Edge As A Service (EAAS) by allowing smaller companies access to the edge resources in order to provide over the top services. This will also drive revenue.

Computing at the edge also requires a networks of hardware that can accept the task request, process it, and send it back to the requester. To develop such smart hardware for the edge computing, the semiconductor companies are comping with low energy and high-performance electronic chips, which can used by the developers to launch new hardware products. All this opens new revenue opportunity for different segments for smaller, mid to high scale enterprises.
The edge computing on top of the smart hardware will increase the adoption rate of the digital services. This will also lead to acquisition of new consumers and will open multiple revenue opportunities.
The edge computing offers exciting benefits and opportunities. Both businesses and consumers are going to be at advantage.
The major application areas that the edge computing is going drive are smart cars, smart cities, smart industry, smart manufacturing, and smart home automation systems.

It will be interesting to see how the industry comes forward and uses the edge computing to launch new digital solutions for the market.
The country which will deploy and adopt the edge computing enabled 5G networks faster is going to be the leader in digital services and information technology for the next decade.