Image Generated Using DALL-E
Semiconductors And PCB
Semiconductors play a crucial role in modern electronic devices by providing processing, memory, and logic functions within microprocessors, memory chips, and integrated circuits. Their precise control of electrical current is essential for today’s complex technology. However, semiconductors require robust support and interconnection infrastructure for practical functionality, where printed circuit boards (PCBs) come into play.
PCBs offer essential physical and electrical support for semiconductors, serving as the platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components. Composed of multiple layers of insulating material and copper traces, PCBs manage signal routing, power distribution, and thermal dissipation to ensure optimal performance of semiconductor devices within a system. The design of PCBs is critical for maintaining signal integrity, reducing electromagnetic interference, and supporting the overall functionality of the electronic assembly.
State Of PCB Industry
The global Printed Circuit Board (PCB) industry has experienced robust growth, driven by the proliferation of consumer electronics, advancements in automotive technology, and the demand for advanced computing systems. The sector, valued at around USD 60 billion in 2023, is projected to maintain steady growth with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4-5% in the coming years. The increasing complexity of electronic devices has led to a surge in demand for high-density interconnect (HDI), flexible, and multi-layer boards, reflecting the industry’s exciting shift towards supporting more sophisticated and compact designs.
Asia holds a significant position in the global PCB industry, with countries like China, Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan leading the production. China, in particular, is the largest producer of PCBs, contributing to more than half of the global output. This dominance is not just about quantity, but also about quality. The region’s abundant raw materials, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and cost advantages ensure that the PCBs produced here are reliable and of high quality. Taiwan and South Korea also play crucial roles, and they are renowned for their expertise in producing high-quality PCBs for advanced applications, especially in the consumer electronics and automotive sectors.
In recent years, the global PCB industry has witnessed a significant shift, with a growing emphasis on reshoring manufacturing in regions like North America and Europe. This strategic move aims to mitigate supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions risks. While Asia remains the primary hub for PCB production, these regions are making substantial investments in developing local capabilities, reducing reliance on foreign suppliers, and bolstering supply chain resilience.
However, the industry faces a talent shortage, particularly in regions outside Asia, where PCB manufacturing has traditionally been concentrated. Yet, companies are not deterred. They are investing in training programs, partnerships with academic institutions, and technology adoption to automate and streamline PCB design and manufacturing processes. This adaptability to new technologies instills optimism about the future of PCB manufacturing. Integrating AI and advanced design tools also helps to bridge the skills gap by automating complex tasks such as [specific tasks] and enabling faster, more accurate PCB development.
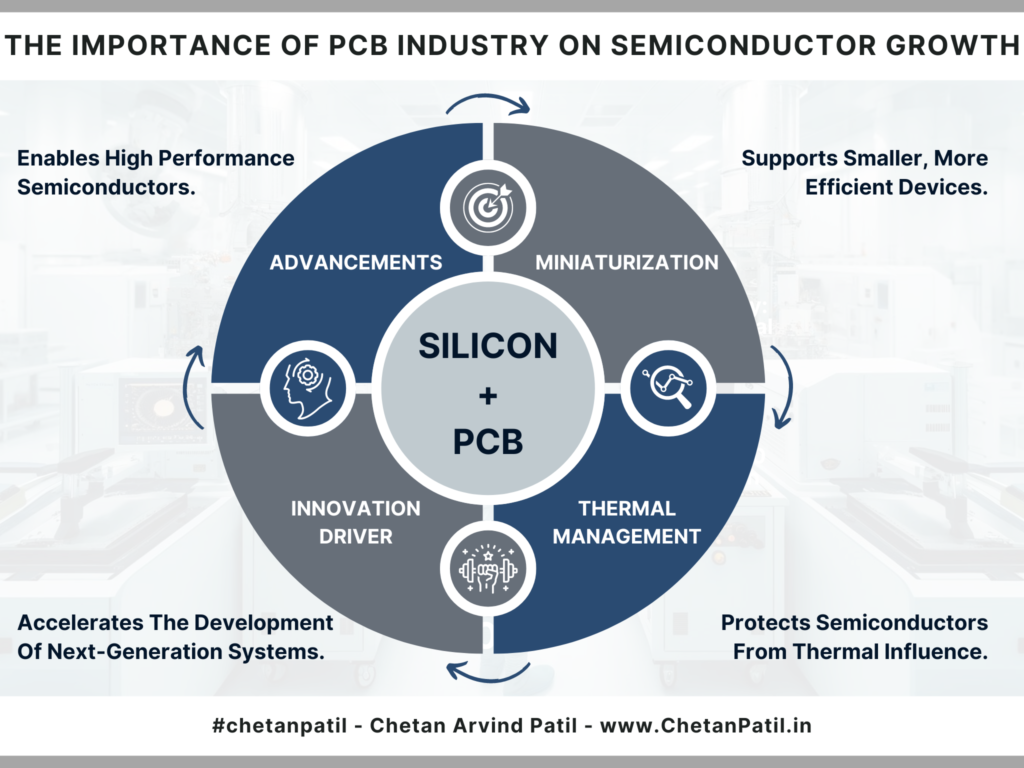
Mutual Reliance Between PCB and Semiconductors
PCBs provide the physical structure and electrical pathways for semiconductors and play a crucial role in the evolution of electronic systems. They ensure proper signal routing, power distribution, and thermal management, which are not just essential but critical for the reliable operation of semiconductor devices.
| Aspect | Impact of PCB Industry on Semiconductor Growth | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Enables Higher Performance Semiconductors | The PCB industry provides the necessary infrastructure (e.g., HDI, multi-layer boards) to support the increasing complexity and performance demands of semiconductor devices. |
| Miniaturization | Supports Smaller, More Efficient Devices | Advanced PCB designs allow for the miniaturization of electronic devices, which is essential for the development of compact and portable semiconductor-based products. |
| Signal Integrity & Power Management | Ensures Reliable Operation of Semiconductor Components | PCBs maintain signal integrity and manage power distribution, which are crucial for the stable and efficient operation of semiconductors in high-performance applications. |
| Thermal Management | Protects Semiconductors from Overheating | Effective thermal management through PCB design prevents overheating, ensuring the longevity and reliability of semiconductor devices. |
| Supply Chain Integration | Facilitates Seamless Production and Integration of Semiconductor Devices | A robust PCB industry ensures that semiconductor manufacturers have a reliable supply chain, allowing for the smooth integration of semiconductors into end-user products. |
| Innovation Driver | Accelerates the Development of Next-Generation Semiconductors | Continuous advancements in PCB technology (e.g., flexible, rigid-flex boards) are essential for enabling new semiconductor innovations, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. |
As semiconductors advance, with higher processing power and smaller form factors, the design and complexity of PCBs must also evolve to support these innovations. This dynamic evolution underscores the significance of PCBs in the electronic system. The semiconductor industry’s growth directly drives demand for more sophisticated and capable PCBs, reflecting the industry’s dynamic nature.
Take Away
The PCB and semiconductor industries are deeply intertwined, relying on each other for continued growth and innovation. Public policies that support the PCB industry are critical for maintaining the health and competitiveness of the semiconductor sector.
By addressing supply chain security, fostering innovation, promoting sustainability, developing the workforce, and enhancing economic competitiveness, governments can ensure that the PCB industry remains vital to technological progress and economic prosperity.