Photo by Raphael GB on Unsplash
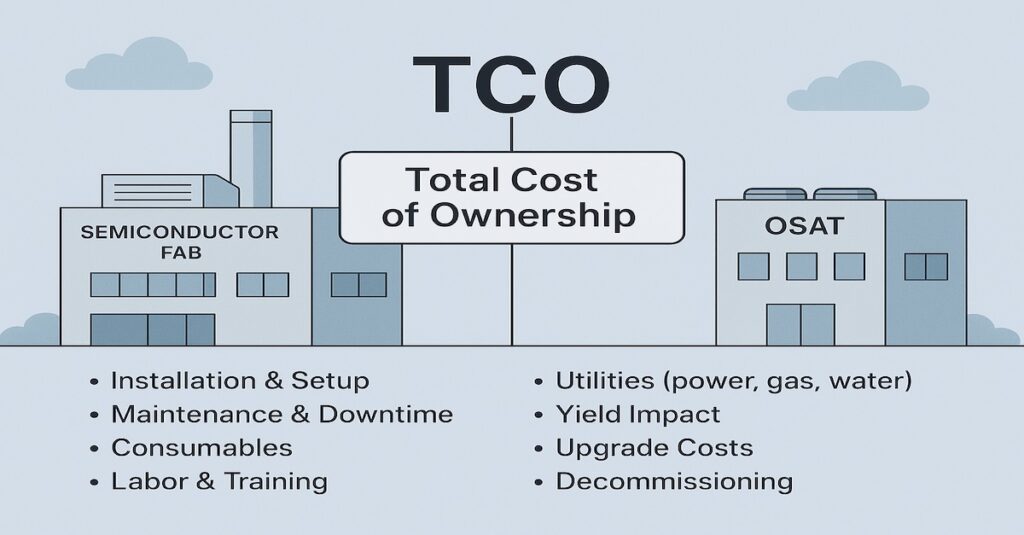
The semiconductor manufacturing business model is changing from FATE to FAST. FATE stands for Fabrication, Assembly, and TEesting, while FAST covers full-flow, i.e., Fabrication, ASsembly, and Testing.
In the FATE model, the fabrication of semiconductor chips is with one specific company, while a different semiconductor manufacturer provides assembly and testing services. In the FAST model, a single semiconductor manufacturer performs all three steps of the manufacturing process.
FATE: Fabrication, Assembly, And TEsting. The Fabrication Of Semiconductor Chips Is With One Specific Company, While A Different Semiconductor Manufacturer Provides Assembly And Testing Services.
There are several reasons why the semiconductor manufacturing business model is changing from FATE to FAST. One reason is that it can help to reduce costs by performing all three steps of the manufacturing process under one roof and, in a few cases, also performing in-house. It can also bring significant cost savings due to turnkey flow, especially for high-volume customers.
Another reason for the shift to FAST is that it can help to improve quality. When a single company performs all three critical steps of the semiconductor manufacturing process, it has more control over the quality of the final product. It can lead to fewer defects and a higher yield.

The shift to FAST can also benefit customers. By having a single point of contact for all three steps of the manufacturing process, customers can streamline their supply chains and reduce the time it takes to get their products to market. It can give them a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Of course, there are also some potential downsides to the FAST model. One concern is that it could decrease innovation and, in many cases, will add extra cost to the manufacturer as the upfront investment to set up such a turnkey facility is very high. If fewer companies are involved in manufacturing, there may be less incentive to develop new and improved technologies, mainly for the aging process, that are still widely used for diverse applications.
FAST: Fabrication, ASsembly, And Testing. Covers Full-Flow. A Single Semiconductor Manufacturer Performs All Three Steps Of The Manufacturing Process.
Another concern is that the FAST model could lead to increased market concentration. If a few large companies control the entire semiconductor manufacturing process, it could be more difficult for new companies to enter the market.
The shift from FATE to FAST can significantly change the semiconductor manufacturing industry. It has the potential to benefit both customers and manufacturers, but there are also some potential downsides to consider. Only time will tell how the FAST model will ultimately impact the industry.